ECB Rate Cuts Shift Focus to Economic Growth in Eurozone
Explore how the ECB's interest rate cuts aim to stimulate economic growth in the eurozone amid easing inflation and stagnant performance.
Key Points
- The ECB has implemented interest rate cuts to shift focus from controlling inflation to stimulating economic growth in the eurozone
.
- Recent economic data shows inflation has eased to 1.7%, but growth remains stagnant, highlighting the need for proactive monetary policy.
- While rate cuts can spur immediate economic activity, addressing structural issues in the eurozone will require broader fiscal reforms and initiatives.
The
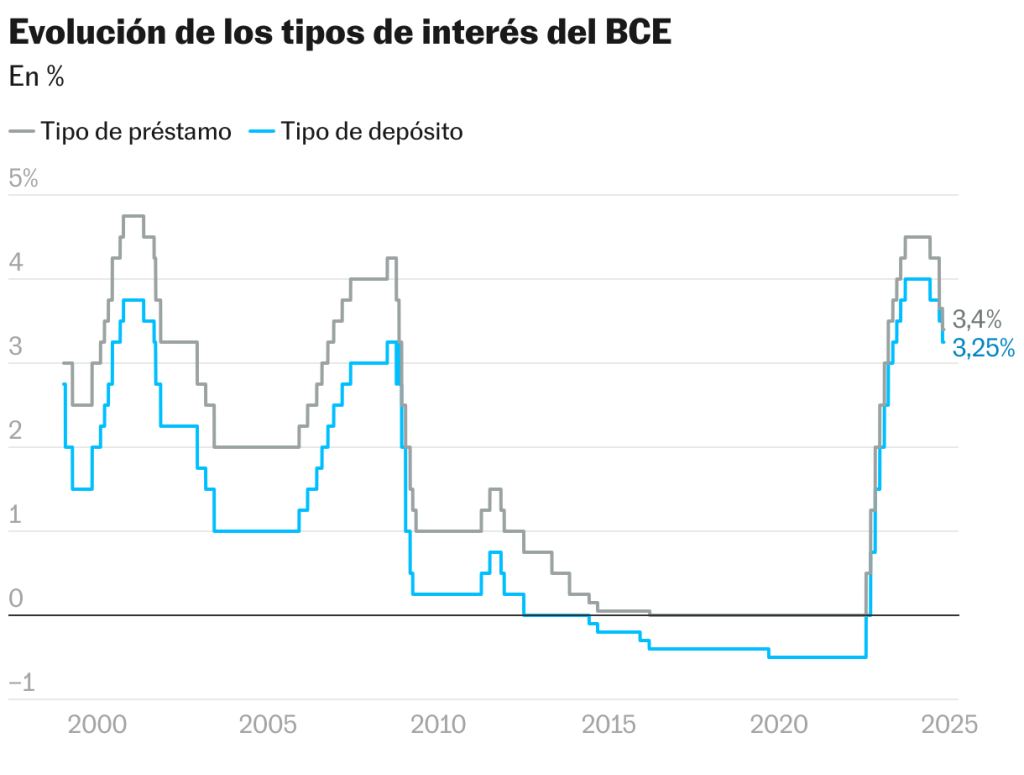
(ECB) has recently made headlines for its decision to implement a series of interest rate cuts, a significant move that signals a shift from prioritizing inflation control to fostering economic growth. This change is especially pertinent as inflation in the eurozone has finally shown signs of easing. With the recent cut to a benchmark rate of 3.25%, the ECB’s actions reflect both the challenges and the opportunities in navigating the current economic landscape.

The Context of Rate Cuts
One of the primary motivations behind the ECB's decision to lower interest rates three times in 2024 is the recent dip in inflation rates. According to recent data, inflation in the eurozone dropped to 1.7% in September, significantly below the ECB's target of 2%. This decline allows the bank to reevaluate its approach, transitioning focus from combating rising prices to reviving an economy that has been struggling. The situation is further complicated by Germany's looming recession, as evidenced by a negative GDP growth rate in the second quarter of this year.
Understanding the Economic Landscape
The economic conditions leading to these rate cuts paint a complex picture. On one hand, the easing of inflation raises hopes for sustained recovery; on the other, growth indicators point to stagnation. The eurozone's growth rate has been unremarkably slow, sitting at a mere 0.2% for the second quarter of the year. This stagnation is not coincidental. The ongoing geopolitical tensions, particularly the conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East, as well as fluctuating energy prices, have undeniably contributed to a more uncertain economic climate.
Moreover, key economic indicators, such as the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), have also sent red flags regarding the health of the manufacturing sector, a critical component of the European economy. As the PMI showed a downturn in manufacturing activities, it became increasingly clear that the ECB needed to act decisively.
A Delicate Balancing Act
The ECB's recent decisions highlight the delicate balancing act central banks must perform. As noted by
, a member of the ECB Board, “Monetary policy cannot resolve structural issues.” Indeed, while interest rate cuts can facilitate liquidity and encourage spending, they cannot directly address the underlying structural challenges within the eurozone economy.
For example, high energy costs and decreasing competitiveness, particularly in Germany, reflect deeper systemic issues that monetary policy alone cannot rectify. Instead, fiscal initiatives and structural reforms may be necessary to bolster economic strength and resilience in the long term.
The Path Ahead
As the ECB steers through these turbulent waters, market observers are closely watching for signals regarding future rate adjustments. The consensus points toward a continued series of cuts, with analysts projecting potential further reductions in subsequent meetings through March 2025. The implicit expectation is that the ECB will maintain a proactive stance, responding to economic data as it becomes available.
In summary, the ECB's recent interest rate cuts signify a strategic pivot to prioritize economic growth amidst a backdrop of subsiding inflation. As the central bank adapts its policies in response to evolving economic indicators, the hope is that these measures will foster a revitalized eurozone economy. However, while immediate monetary actions can stimulate growth, addressing the structural challenges within the eurozone remains a broader and more complex undertaking. The path ahead may be fraught with challenges, but the ECB’s commitment to monitoring and responding to economic conditions will be vital in navigating these uncharted territories.


